Skin Rejuvenation
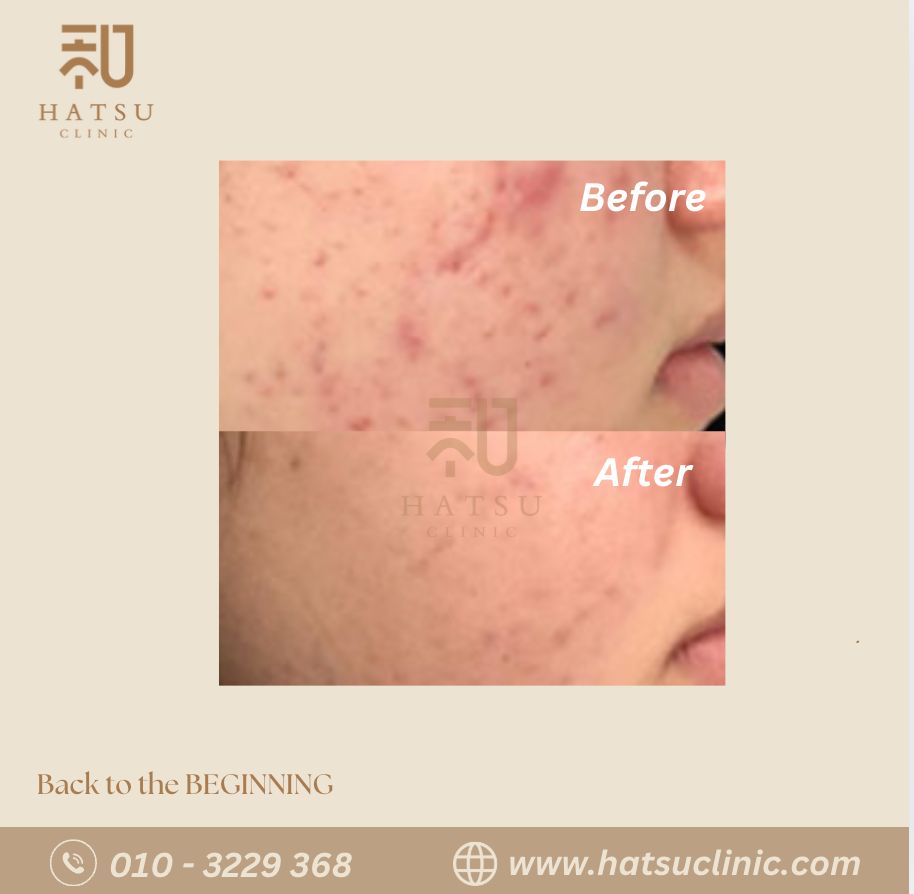
Acne & Acne Scar Treatment
Acne (acne vulgaris) is a very common skin condition that affects both teenagers and adults.
It develops when pores become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to inflammation and breakouts.
If not treated early or properly, acne can progress to deeper lesions and eventually leave scars.
Understanding the type of acne is essential for effective treatment.
Types of Acne
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne (Comedonal)
Includes:
whiteheads
blackheads
Caused by clogged pores without significant redness or swelling.
2. Inflammatory Acne
Includes:
papules
pustules
painful nodules
These lesions are red and swollen, often indicating deeper inflammation.
3. Cystic Acne
A severe form involving:
deep, painful cysts
significant inflammation
high risk of scarring
Requires prompt medical treatment to prevent long-term damage.
What Causes Acne?
Acne can be triggered or worsened by:
genetics
hormonal fluctuations (e.g., puberty, menstrual cycles)
stress
unhealthy diet or high-glycemic foods
environmental pollution
certain skincare or medications
A thorough assessment helps determine the primary cause and design a suitable treatment plan.
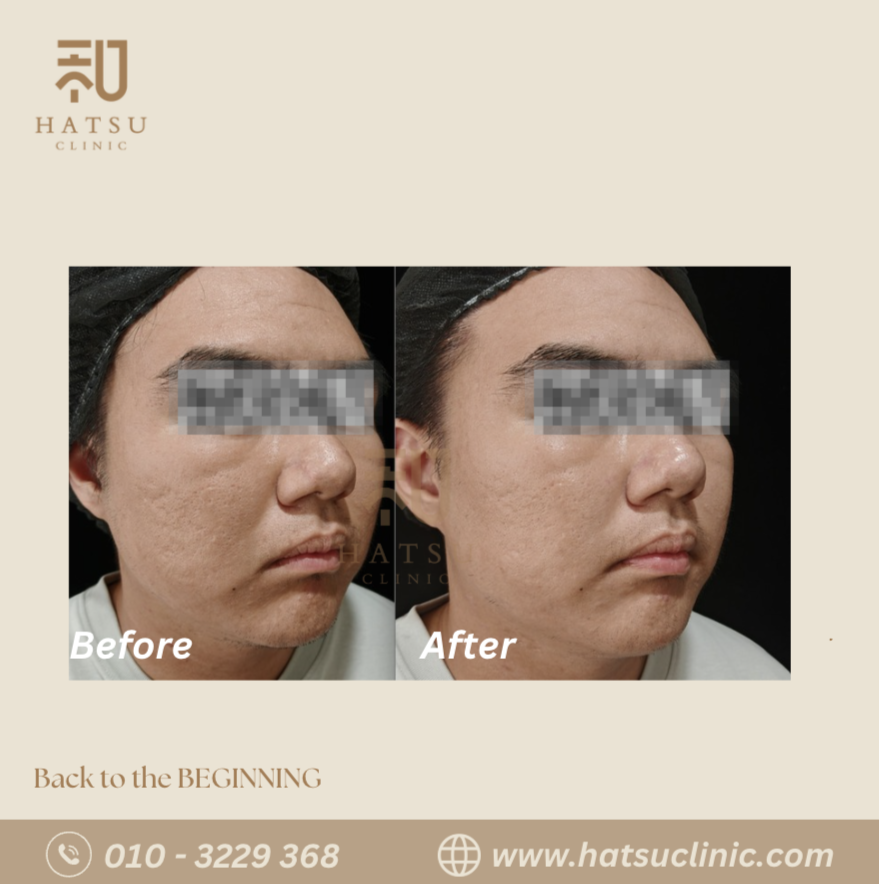
Acne Scars
Acne scars often develop when deep inflammation damages the skin’s collagen.
Different scar types require different treatments.
Types of Acne Scars
1. Ice Pick Scars
Deep, narrow scars that look like small punctures in the skin.
2. Boxcar Scars
Shallow or moderately deep depressions with sharp edges.
3. Rolling Scars
Wave-like, broad depressions caused by tethered scar tissue.
4. Hypertrophic Scars
Raised, firm scars that form when too much collagen is produced.
Treatments for Acne & Acne Scars
Each treatment targets different severity levels and scar types.
All procedures are performed or supervised by our LCP-certified doctor.
1. Radiofrequency Microneedling
Stimulates deep collagen remodeling to:
reduce acne scars
tighten skin
smooth uneven texture
Highly effective for rolling, boxcar, and mixed scars.
2. Fractional Laser
Creates controlled micro-injuries to:
resurface skin
improve texture
lighten pigmentation
stimulate collagen repair
Suitable for moderate acne scars and skin resurfacing.
3. Pico Laser
Targets:
post-acne pigmentation
redness
uneven skin tone
Speeds up the fading of dark acne marks.
4. Chemical Peel
Exfoliates clogged pores and reduces:
comedonal acne
mild acne
surface irregularities
Helps improve skin clarity and smoothness.
5. Microneedling
Improves:
mild acne scars
enlarged pores
skin texture
A collagen-stimulating treatment with minimal downtime.
6. PRP / PRF (Regenerative Therapy)
Uses your body’s growth factors to:
accelerate healing
improve scar texture
reduce redness
enhance collagen production
Often combined with microneedling or RF.
7. Plenhyage (Polynucleotide Therapy)
Repairs damaged skin and improves:
rough texture
atrophic scars
post-inflammatory pigmentation
Supports dermal regeneration.
8. TCA Cross & Subcision
Advanced techniques for deep scars:
TCA Cross: chemical reconstruction of ice pick scars
Subcision: releases tethered rolling scars for visible elevation
Often paired with laser or RF for optimal results.
FAQ
1. What is the best treatment for acne scars?
It depends on scar type. Many cases require combination therapy.
2. Can acne be treated permanently?
Acne can be controlled effectively with the right approach and maintenance plan.
3. When will I see results?
Improvement can be seen after several sessions, with continued progress over months as collagen rebuilds.
4. Is downtime required?
Varies by treatment — from minimal downtime (microneedling) to a few days (fractional laser or TCA).


Dull Complexion Treatment
A dull complexion occurs when the skin loses its natural glow and appears tired, uneven, or lackluster.
This can happen at any age and is often caused by pigmentation, dehydration, and slowed skin renewal.
Understanding the underlying factors helps determine the most effective treatment approach.
What Causes a Dull Complexion?
1. Melanin Deposition (Sun-Induced Pigmentation)
UV exposure triggers excess melanin production, leading to:
dark spots
uneven skin tone
overall darker appearance
This is one of the most common causes of dull-looking skin.
2. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
After acne, eczema, or skin irritation, damaged areas may develop:
brown marks
red marks
blemish shadows
These patches reduce skin brightness and create an uneven tone.
3. Aging
As collagen, elastin, and skin renewal slow down with age, the skin becomes:
less radiant
rougher
less able to reflect light
This contributes to a tired or aged appearance.
4. UV Damage
Prolonged sun exposure breaks down collagen and increases pigmentation.
The result:
sagging
wrinkles
dull, uneven skin
UV protection is essential for maintaining radiance.
5. Dehydration
When the skin lacks moisture, it appears:
flat
rough
dry
Hydrated skin reflects light better, giving a healthy glow.
6. Dead Skin Buildup
Accumulated dead cells prevent fresh skin from showing through, causing:
rough texture
uneven tone
dullness
Regular exfoliation helps restore clarity.
Can Dull Skin Be Improved?
Yes. A combination of brightening, resurfacing, and collagen-stimulating treatments can restore clarity and radiance.
Lifestyle adjustments such as hydration and sun protection also play a key role.
Treatments for Dull Complexion
1. Pico Laser
Targets:
pigmentation
melanin buildup
uneven tone
Improves overall brightness and clarity with minimal downtime.
2. Chemical Peel
Gently exfoliates the skin to:
remove dead cells
brighten skin tone
smooth rough texture
A great option for early dullness.
3. Skinvive Skin Booster
A hydrating micro-droplet treatment that:
deeply moisturizes the skin
enhances natural radiance
softens fine lines
improves overall glow
Ideal for dry and tired-looking skin.
4. Cellbooster Lift
A bio-revitalization treatment that:
improves firmness
brightens dull tone
boosts collagen and elasticity
Suitable for mature or stressed skin.
5. Xela Rederm Skin Booster
Designed to:
reduce pigmentation
improve hydration
enhance overall skin luminosity
Perfect for dullness caused by aging or UV damage.
FAQ
1. How long does it take to see improvement?
Many patients see brighter skin after 1–2 sessions, with continued improvement over several weeks.
2. Which treatment is best for dull skin?
It depends on the cause—pigmentation, dehydration, or aging. A consultation helps determine the right plan.
3. Is downtime required?
Most treatments have minimal downtime and allow you to return to daily activities quickly.
4. Can dull skin return?
Yes, without sun protection and hydration. Maintenance treatments keep the glow long-term.
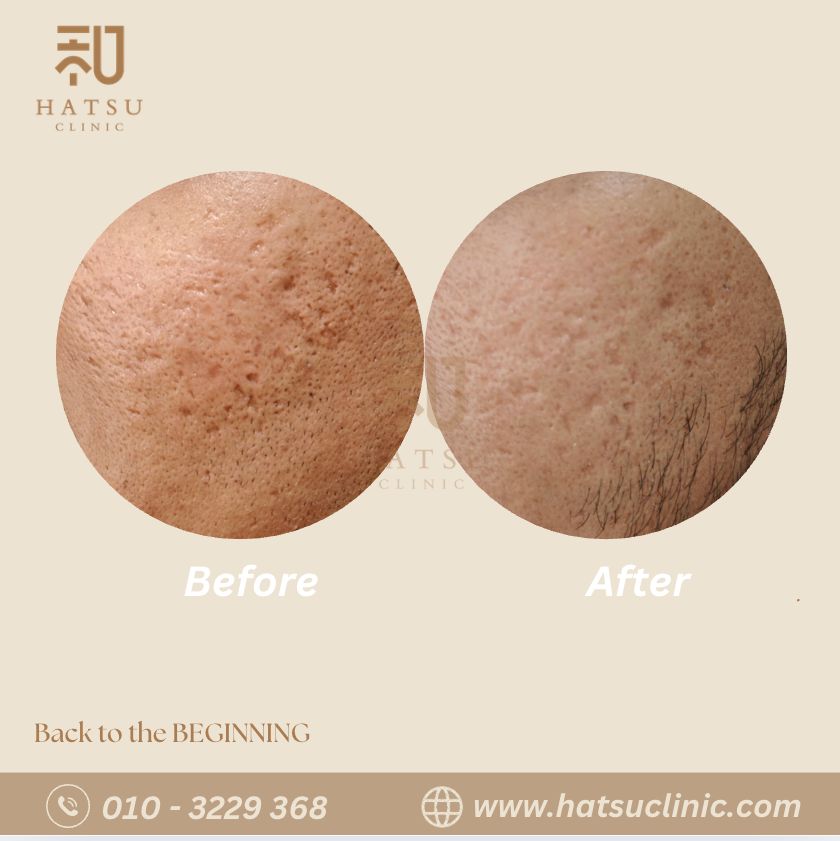
Enlarged Pores Treatment
Enlarged pores are a very common skin concern.
Pores are natural openings that release oil and sweat — but when they expand, they can make the skin look uneven, rough, and less refined.
They commonly appear on the nose, cheeks, forehead, and T-zone.
Although pores cannot be permanently “removed,” their appearance can be significantly minimized with the right treatments.
What Causes Enlarged Pores?
1. Excess Sebum Production (Oily Skin)
Overactive oil glands mix with dead skin cells and clog pores.
Blocked pores stretch, making them appear larger and more visible.
2. Aging and Collagen Loss
As skin ages, collagen and elastin gradually decrease.
This weakens pore walls, causing them to:
sag
stretch
appear larger over time
3. Sun Damage
UV exposure:
breaks down collagen
thickens the surface of the skin
reduces elasticity
All of these make pores look bigger and more noticeable.
4. Genetics
Some individuals naturally have:
larger pores
thicker or oilier skin
These traits often run in families.
5. Clogged Pores
When pores are filled with:
oil
dead skin
dirt
makeup residue
they expand and lose their ability to return to their normal size.
Can Enlarged Pores Be Improved?
Yes. While pores cannot be permanently shrunk, their visible size can be dramatically reduced with treatments that:
regulate oil production
stimulate collagen
resurface the skin
tighten pore openings
A combination approach often yields the best results.
Treatments for Enlarged Pores
1. Radiofrequency Microneedling
Stimulates deep collagen remodeling to:
tighten pore walls
reduce pore size
smooth skin texture
Highly effective for sagging or aging pores.
2. Fractional Laser
Resurfaces the top layer of skin to:
refine texture
unclog pores
stimulate new collagen
Suitable for pores caused by sun damage or scarring.
3. Microneedling
Creates micro-injuries that promote collagen production and:
tighten pores
improve surface smoothness
enhance skin clarity
Good for mild to moderate pore enlargement.
4. Polynucleotide Plenhyage
A regenerative treatment that:
boosts collagen
improves skin elasticity
strengthens pore structure
enhances overall skin quality
Beneficial for thin or aging pore-prone skin.
5. Linerase Collagen Booster
Stimulates collagen to:
firm the skin
refine enlarged pores
improve skin density
Ideal for mature or weakened skin.
6. MesoBotox
Micro-dosed botulinum toxin applied superficially to:
reduce oil production
tighten pore openings
create a smooth, matte finish
Popular for oily T-zone and event-prep treatments.
FAQ
1. Can pores be completely closed?
No — pores are natural structures, but their appearance can be minimized significantly.
2. How long until I see improvement?
Many patients notice smoother skin within a few weeks, with continued improvement as collagen builds.
3. Which treatment works best?
It depends on the cause: oiliness, aging, sun damage, or clogged pores.
4. Is downtime required?
Minimal. Some treatments may cause mild redness for 1–2 days.
Fine Lines & Wrinkles Treatment
Fine lines and wrinkles are among the earliest and most visible signs of aging.
They commonly appear as:
-
crow’s feet
-
forehead lines
-
frown lines
-
smile lines
-
nasolabial folds
These changes occur gradually but can be effectively improved with modern aesthetic treatments.
What Causes Fine Lines & Wrinkles?
1. Reduced Collagen and Elastin
As we age, the skin naturally produces less collagen (for firmness) and elastin (for elasticity).
When these supportive fibers decline, the skin becomes:
-
thinner
-
less supple
-
more prone to folding and creasing
This leads to fine lines and eventually deeper wrinkles.
2. Repetitive Facial Expressions
Daily expressions — smiling, frowning, squinting, raising brows — create repeated muscle movements.
Over time, these movements form dynamic wrinkles, which may later become permanent.
3. Sun Exposure (Photoaging)
UV rays accelerate the breakdown of collagen and elastin.
Long-term exposure leads to:
-
fine lines
-
wrinkles
-
roughness
-
sagging
-
uneven tone
Sun protection is crucial for slowing visible aging.
4. Dehydration
Lack of moisture makes the skin:
-
dry
-
fragile
-
less resilient
Dehydrated skin shows fine lines more easily, especially around the delicate eye area.
Can Fine Lines & Wrinkles Be Improved?
Yes. With targeted treatments that stimulate collagen, relax overactive muscles, and restore volume, the skin can appear smoother, firmer, and more youthful.
A personalized plan ensures natural, balanced results.
Wrinkle & Anti-Aging Treatments
1. BTL Exion (RF + Collagen Stimulation)
Non-invasive treatment that:
-
improves skin elasticity
-
softens fine lines
-
enhances overall skin firmness
Ideal for early aging or maintenance.
2. Radiofrequency Microneedling
Stimulates deep collagen remodeling to:
-
smooth fine and moderate wrinkles
-
tighten lax skin
-
improve texture
Effective for crepey skin and deeper facial lines.
3. Fractional Laser
Resurfaces the skin and:
-
improves texture
-
reduces fine lines
-
restores brightness
A strong option for photoaging and rough skin.
4. Microneedling
Boosts collagen naturally and improves:
-
fine lines
-
mild texture issues
-
early aging signs
Gentle option with minimal downtime.
5. Botulinum Toxin Injection
Temporarily relaxes facial muscles to smooth:
-
frown lines
-
forehead lines
-
crow’s feet
Prevents lines from deepening and maintains a refreshed look.
6. Linerase Collagen Booster
Bio-stimulation treatment that:
-
thickens the skin
-
improves elasticity
-
softens fine lines
Ideal for aging, thin, or dehydrated skin.
7. Dermal Filler
Restores lost volume and smooths:
-
nasolabial folds
-
marionette lines
-
deep wrinkles
Also enhances facial contour and support for a youthful appearance.
FAQ
1. When should I start anti-aging treatments?
Prevention can start in your 20s–30s, but improvements are effective at any age.
2. How many sessions do I need?
Most treatments require several sessions for optimal results, depending on severity.
3. Do results look natural?
Yes. Treatments are carefully tailored to maintain your natural expression and features.
4. Is downtime required?
Botulinum toxin has no downtime; lasers and microneedling may require 1–3 days.




